API&时间类&异常&Optional
提示
Java基础语法,博主看的黑马的视频。
# 1.时间日期类
# 1.1 Date类
计算机中时间原点
1970年1月1日 00:00:00
时间换算单位
1秒 = 1000毫秒
Date类概述
Date 代表了一个特定的时间,精确到毫秒
Date类构造方法
方法名 说明 public Date() 分配一个 Date对象,并初始化,以便它代表它被分配的时间,精确到毫秒 public Date(long date) 分配一个 Date对象,并将其初始化为表示从标准基准时间起指定的毫秒数 示例代码
public class DateDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //public Date():分配一个 Date对象,并初始化,以便它代表它被分配的时间,精确到毫秒 Date d1 = new Date(); System.out.println(d1); //public Date(long date):分配一个 Date对象,并将其初始化为表示从标准基准时间起指定的毫秒数 long date = 1000*60*60; Date d2 = new Date(date); System.out.println(d2); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 1.2 Date类常用方法
常用方法
方法名 说明 public long getTime() 获取的是日期对象从1970年1月1日 00:00:00到现在的毫秒值 public void setTime(long time) 设置时间,给的是毫秒值 示例代码
public class DateDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建日期对象 Date d = new Date(); //public long getTime():获取的是日期对象从1970年1月1日 00:00:00到现在的毫秒值 // System.out.println(d.getTime()); // System.out.println(d.getTime() * 1.0 / 1000 / 60 / 60 / 24 / 365 + "年"); //public void setTime(long time):设置时间,给的是毫秒值 // long time = 1000*60*60; long time = System.currentTimeMillis(); d.setTime(time); System.out.println(d); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 1.3 SimpleDateFormat类
SimpleDateFormat类概述
SimpleDateFormat是一个具体的类,用于以区域设置敏感的方式格式化和解析日期。
我们重点学习日期格式化和解析
SimpleDateFormat类构造方法
方法名 说明 public SimpleDateFormat() 构造一个SimpleDateFormat,使用默认模式和日期格式 public SimpleDateFormat(String pattern) 构造一个SimpleDateFormat使用给定的模式和默认的日期格式 SimpleDateFormat类的常用方法
- 格式化(从Date到String)
- public final String format(Date date):将日期格式化成日期/时间字符串
- 解析(从String到Date)
- public Date parse(String source):从给定字符串的开始解析文本以生成日期
- 格式化(从Date到String)
示例代码
public class SimpleDateFormatDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException { //格式化:从 Date 到 String Date d = new Date(); // SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(); SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss"); String s = sdf.format(d); System.out.println(s); System.out.println("--------"); //从 String 到 Date String ss = "2048-08-09 11:11:11"; //ParseException SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); Date dd = sdf2.parse(ss); System.out.println(dd); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 1.4 时间日期类练习
需求
秒杀开始时间是2020年11月11日 00:00:00,结束时间是2020年11月11日 00:10:00,用户小贾下单时间是2020年11月11日 00:03:47,用户小皮下单时间是2020年11月11日 00:10:11,判断用户有没有成功参与秒杀活动
实现步骤
- 判断下单时间是否在开始到结束的范围内
- 把字符串形式的时间变成毫秒值
代码实现
public class DateDemo5 { public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException { //开始时间:2020年11月11日 0:0:0 //结束时间:2020年11月11日 0:10:0 //小贾2020年11月11日 0:03:47 //小皮2020年11月11日 0:10:11 //1.判断两位同学的下单时间是否在范围之内就可以了。 //2.要把每一个时间都换算成毫秒值。 String start = "2020年11月11日 0:0:0"; String end = "2020年11月11日 0:10:0"; String jia = "2020年11月11日 0:03:47"; String pi = "2020年11月11日 0:10:11"; SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss"); long startTime = sdf.parse(start).getTime(); long endTime = sdf.parse(end).getTime(); // System.out.println(startTime); // System.out.println(endTime); long jiaTime = sdf.parse(jia).getTime(); long piTime = sdf.parse(pi).getTime(); if(jiaTime >= startTime && jiaTime <= endTime){ System.out.println("小贾同学参加上了秒杀活动"); }else{ System.out.println("小贾同学没有参加上秒杀活动"); } System.out.println("------------------------"); if(piTime >= startTime && piTime <= endTime){ System.out.println("小皮同学参加上了秒杀活动"); }else{ System.out.println("小皮同学没有参加上秒杀活动"); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
# 2.JDK8时间日期类
# 2.1 JDK8新增日期类
- LocalDate 表示日期(年月日)
- LocalTime 表示时间(时分秒)
- LocalDateTime 表示时间+ 日期 (年月日时分秒)
# 2.2 LocalDateTime创建方法
方法说明
方法名 说明 public static LocalDateTime now() 获取当前系统时间 public static LocalDateTime of (年, 月 , 日, 时, 分, 秒) 使用指定年月日和时分秒初始化一个LocalDateTime对象 示例代码
public class JDK8DateDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now(); System.out.println(now); LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11); System.out.println(localDateTime); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 2.3 LocalDateTime获取方法
方法说明
方法名 说明 public int getYear() 获取年 public int getMonthValue() 获取月份(1-12) public int getDayOfMonth() 获取月份中的第几天(1-31) public int getDayOfYear() 获取一年中的第几天(1-366) public DayOfWeek getDayOfWeek() 获取星期 public int getMinute() 获取分钟 public int getHour() 获取小时 示例代码
public class JDK8DateDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 11, 11, 11, 11, 20); //public int getYear() 获取年 int year = localDateTime.getYear(); System.out.println("年为" +year); //public int getMonthValue() 获取月份(1-12) int month = localDateTime.getMonthValue(); System.out.println("月份为" + month); Month month1 = localDateTime.getMonth(); // System.out.println(month1); //public int getDayOfMonth() 获取月份中的第几天(1-31) int day = localDateTime.getDayOfMonth(); System.out.println("日期为" + day); //public int getDayOfYear() 获取一年中的第几天(1-366) int dayOfYear = localDateTime.getDayOfYear(); System.out.println("这是一年中的第" + dayOfYear + "天"); //public DayOfWeek getDayOfWeek()获取星期 DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = localDateTime.getDayOfWeek(); System.out.println("星期为" + dayOfWeek); //public int getMinute() 获取分钟 int minute = localDateTime.getMinute(); System.out.println("分钟为" + minute); //public int getHour() 获取小时 int hour = localDateTime.getHour(); System.out.println("小时为" + hour); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# 2.4 LocalDateTime转换方法
方法说明
方法名 说明 public LocalDate toLocalDate () 转换成为一个LocalDate对象 public LocalTime toLocalTime () 转换成为一个LocalTime对象 示例代码
public class JDK8DateDemo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 12, 12, 8, 10, 12); //public LocalDate toLocalDate () 转换成为一个LocalDate对象 LocalDate localDate = localDateTime.toLocalDate(); System.out.println(localDate); //public LocalTime toLocalTime () 转换成为一个LocalTime对象 LocalTime localTime = localDateTime.toLocalTime(); System.out.println(localTime); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 2.5 LocalDateTime格式化和解析
方法说明
方法名 说明 public String format (指定格式) 把一个LocalDateTime格式化成为一个字符串 public LocalDateTime parse (准备解析的字符串, 解析格式) 把一个日期字符串解析成为一个LocalDateTime对象 public static DateTimeFormatter ofPattern(String pattern) 使用指定的日期模板获取一个日期格式化器DateTimeFormatter对象 示例代码
public class JDK8DateDemo5 { public static void main(String[] args) { //method1(); //method2(); } private static void method2() { //public static LocalDateTime parse (准备解析的字符串, 解析格式) 把一个日期字符串解析成为一个LocalDateTime对象 String s = "2020年11月12日 13:14:15"; DateTimeFormatter pattern = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss"); LocalDateTime parse = LocalDateTime.parse(s, pattern); System.out.println(parse); } private static void method1() { LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15); System.out.println(localDateTime); //public String format (指定格式) 把一个LocalDateTime格式化成为一个字符串 DateTimeFormatter pattern = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss"); String s = localDateTime.format(pattern); System.out.println(s); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 2.6 LocalDateTime增加或者减少时间的方法
方法说明
方法名 说明 public LocalDateTime plusYears (long years) 添加或者减去年 public LocalDateTime plusMonths(long months) 添加或者减去月 public LocalDateTime plusDays(long days) 添加或者减去日 public LocalDateTime plusHours(long hours) 添加或者减去时 public LocalDateTime plusMinutes(long minutes) 添加或者减去分 public LocalDateTime plusSeconds(long seconds) 添加或者减去秒 public LocalDateTime plusWeeks(long weeks) 添加或者减去周 示例代码
/** * JDK8 时间类添加或者减去时间的方法 */ public class JDK8DateDemo6 { public static void main(String[] args) { //public LocalDateTime plusYears (long years) 添加或者减去年 LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 11, 11, 13, 14, 15); //LocalDateTime newLocalDateTime = localDateTime.plusYears(1); //System.out.println(newLocalDateTime); LocalDateTime newLocalDateTime = localDateTime.plusYears(-1); System.out.println(newLocalDateTime); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 2.7 LocalDateTime减少或者增加时间的方法
方法说明
方法名 说明 public LocalDateTime minusYears (long years) 减去或者添加年 public LocalDateTime minusMonths(long months) 减去或者添加月 public LocalDateTime minusDays(long days) 减去或者添加日 public LocalDateTime minusHours(long hours) 减去或者添加时 public LocalDateTime minusMinutes(long minutes) 减去或者添加分 public LocalDateTime minusSeconds(long seconds) 减去或者添加秒 public LocalDateTime minusWeeks(long weeks) 减去或者添加周 示例代码
/** * JDK8 时间类减少或者添加时间的方法 */ public class JDK8DateDemo7 { public static void main(String[] args) { //public LocalDateTime minusYears (long years) 减去或者添加年 LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 11, 11, 13, 14, 15); //LocalDateTime newLocalDateTime = localDateTime.minusYears(1); //System.out.println(newLocalDateTime); LocalDateTime newLocalDateTime = localDateTime.minusYears(-1); System.out.println(newLocalDateTime); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 2.8 LocalDateTime修改方法
方法说明
方法名 说明 public LocalDateTime withYear(int year) 直接修改年 public LocalDateTime withMonth(int month) 直接修改月 public LocalDateTime withDayOfMonth(int dayofmonth) 直接修改日期(一个月中的第几天) public LocalDateTime withDayOfYear(int dayOfYear) 直接修改日期(一年中的第几天) public LocalDateTime withHour(int hour) 直接修改小时 public LocalDateTime withMinute(int minute) 直接修改分钟 public LocalDateTime withSecond(int second) 直接修改秒 示例代码
/** * JDK8 时间类修改时间 */ public class JDK8DateDemo8 { public static void main(String[] args) { //public LocalDateTime withYear(int year) 修改年 LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 11, 11, 13, 14, 15); // LocalDateTime newLocalDateTime = localDateTime.withYear(2048); // System.out.println(newLocalDateTime); LocalDateTime newLocalDateTime = localDateTime.withMonth(20); System.out.println(newLocalDateTime); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 2.9 Period
方法说明
方法名 说明 public static Period between(开始时间,结束时间) 计算两个“时间"的间隔 public int getYears() 获得这段时间的年数 public int getMonths() 获得此期间的总月数 public int getDays() 获得此期间的天数 public long toTotalMonths() 获取此期间的总月数 示例代码
/** * 计算两个时间的间隔 */ public class JDK8DateDemo9 { public static void main(String[] args) { //public static Period between(开始时间,结束时间) 计算两个"时间"的间隔 LocalDate localDate1 = LocalDate.of(2020, 1, 1); LocalDate localDate2 = LocalDate.of(2048, 12, 12); Period period = Period.between(localDate1, localDate2); System.out.println(period);//P28Y11M11D //public int getYears() 获得这段时间的年数 System.out.println(period.getYears());//28 //public int getMonths() 获得此期间的月数 System.out.println(period.getMonths());//11 //public int getDays() 获得此期间的天数 System.out.println(period.getDays());//11 //public long toTotalMonths() 获取此期间的总月数 System.out.println(period.toTotalMonths());//347 } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 2.10 Duration
方法说明
方法名 说明 public static Durationbetween(开始时间,结束时间) 计算两个“时间"的间隔 public long toSeconds() 获得此时间间隔的秒 public int toMillis() 获得此时间间隔的毫秒 public int toNanos() 获得此时间间隔的纳秒 示例代码
/** * 计算两个时间的间隔 */ public class JDK8DateDemo10 { public static void main(String[] args) { //public static Duration between(开始时间,结束时间) 计算两个“时间"的间隔 LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 1, 1, 13, 14, 15); LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 1, 2, 11, 12, 13); Duration duration = Duration.between(localDateTime1, localDateTime2); System.out.println(duration);//PT21H57M58S //public long toSeconds() 获得此时间间隔的秒 System.out.println(duration.toSeconds());//79078 //public int toMillis() 获得此时间间隔的毫秒 System.out.println(duration.toMillis());//79078000 //public int toNanos() 获得此时间间隔的纳秒 System.out.println(duration.toNanos());//79078000000000 } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 3.异常
# 3.1 异常
异常的概述
异常就是程序出现了不正常的情况
异常的体系结构
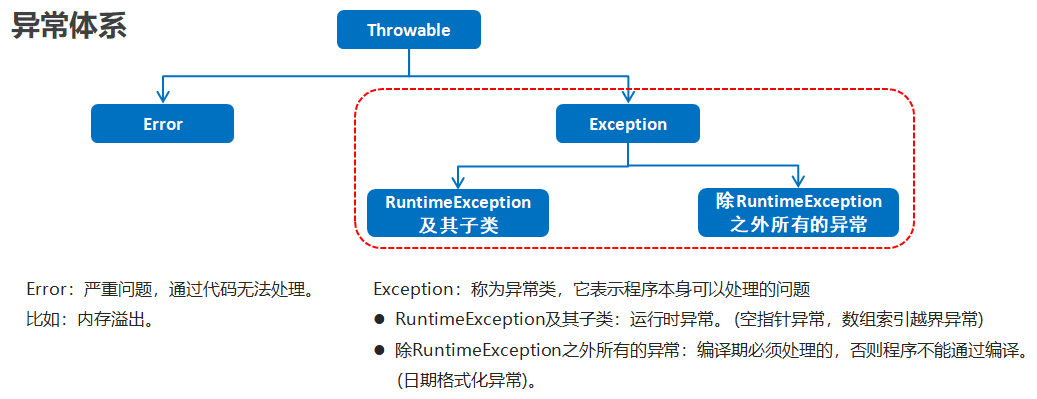
# 3.2 编译时异常和运行时异常的区别
编译时异常
- 都是Exception类及其子类
- 必须显示处理,否则程序就会发生错误,无法通过编译
运行时异常
- 都是RuntimeException类及其子类
- 无需显示处理,也可以和编译时异常一样处理
图示

# 3.3 JVM默认处理异常的方式
- 如果程序出现了问题,我们没有做任何处理,最终JVM 会做默认的处理,处理方式有如下两个步骤:
- 把异常的名称,错误原因及异常出现的位置等信息输出在了控制台
- 程序停止执行
# 3.4 查看异常信息
控制台在打印异常信息时,会打印异常类名,异常出现的原因,异常出现的位置
我们调bug时,可以根据提示,找到异常出现的位置,分析原因,修改异常代码

# 3.5 throws方式处理异常
定义格式
public void 方法() throws 异常类名 { }1
2
3示例代码
public class ExceptionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException{ System.out.println("开始"); // method(); method2(); System.out.println("结束"); } //编译时异常 public static void method2() throws ParseException { String s = "2048-08-09"; SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); Date d = sdf.parse(s); System.out.println(d); } //运行时异常 public static void method() throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException { int[] arr = {1, 2, 3}; System.out.println(arr[3]); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23注意事项
- 这个throws格式是跟在方法的括号后面的
- 编译时异常必须要进行处理,两种处理方案:try...catch …或者 throws,如果采用 throws 这种方案,在方法上进行显示声明,将来谁调用这个方法谁处理
- 运行时异常因为在运行时才会发生,所以在方法后面可以不写,运行时出现异常默认交给jvm处理
# 3.6 throw抛出异常
格式
throw new 异常();
注意
这个格式是在方法内的,表示当前代码手动抛出一个异常,下面的代码不用再执行了
throws和throw的区别
throws throw 用在方法声明后面,跟的是异常类名 用在方法体内,跟的是异常对象名 表示声明异常,调用该方法有可能会出现这样的异常 表示手动抛出异常对象,由方法体内的语句处理 示例代码
public class ExceptionDemo8 { public static void main(String[] args) { //int [] arr = {1,2,3,4,5}; int [] arr = null; printArr(arr);//就会 接收到一个异常. //我们还需要自己处理一下异常. } private static void printArr(int[] arr) { if(arr == null){ //调用者知道成功打印了吗? //System.out.println("参数不能为null"); throw new NullPointerException(); //当参数为null的时候 //手动创建了一个异常对象,抛给了调用者,产生了一个异常 }else{ for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.println(arr[i]); } } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 3.7 try-catch方式处理异常
定义格式
try { 可能出现异常的代码; } catch(异常类名 变量名) { 异常的处理代码; }1
2
3
4
5执行流程
- 程序从 try 里面的代码开始执行
- 出现异常,就会跳转到对应的 catch 里面去执行
- 执行完毕之后,程序还可以继续往下执行
示例代码
public class ExceptionDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("开始"); method(); System.out.println("结束"); } public static void method() { try { int[] arr = {1, 2, 3}; System.out.println(arr[3]); System.out.println("这里能够访问到吗"); } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println("你访问的数组索引不存在,请回去修改为正确的索引"); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17注意
如果 try 中没有遇到问题,怎么执行?
会把try中所有的代码全部执行完毕,不会执行catch里面的代码
如果 try 中遇到了问题,那么 try 下面的代码还会执行吗?
那么直接跳转到对应的catch语句中,try下面的代码就不会再执行了 当catch里面的语句全部执行完毕,表示整个体系全部执行完全,继续执行下面的代码
如果出现的问题没有被捕获,那么程序如何运行?
那么try...catch就相当于没有写.那么也就是自己没有处理. 默认交给虚拟机处理.
同时有可能出现多个异常怎么处理?
出现多个异常,那么就写多个catch就可以了. 注意点:如果多个异常之间存在子父类关系.那么父类一定要写在下面
# 3.8 Throwable成员方法
常用方法
方法名 说明 public String getMessage() 返回此 throwable 的详细消息字符串 public String toString() 返回此可抛出的简短描述 public void printStackTrace() 把异常的错误信息输出在控制台 示例代码
public class ExceptionDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("开始"); method(); System.out.println("结束"); } public static void method() { try { int[] arr = {1, 2, 3}; System.out.println(arr[3]); //new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); System.out.println("这里能够访问到吗"); } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { //new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); // e.printStackTrace(); //public String getMessage():返回此 throwable 的详细消息字符串 // System.out.println(e.getMessage()); //Index 3 out of bounds for length 3 //public String toString():返回此可抛出的简短描述 // System.out.println(e.toString()); //java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 3 out of bounds for length 3 //public void printStackTrace():把异常的错误信息输出在控制台 e.printStackTrace(); // java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 3 out of bounds for length 3 // at com.itheima_02.ExceptionDemo02.method(ExceptionDemo02.java:18) // at com.itheima_02.ExceptionDemo02.main(ExceptionDemo02.java:11) } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# 3.9 异常的练习
需求
键盘录入学生的姓名和年龄,其中年龄为18 - 25岁,超出这个范围是异常数据不能赋值.需要重新录入,一直录到正确为止
实现步骤
- 创建学生对象
- 键盘录入姓名和年龄,并赋值给学生对象
- 如果是非法数据就再次录入
代码实现
学生类
public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { if(age >= 18 && age <= 25){ this.age = age; }else{ //当年龄不合法时,产生一个异常 throw new RuntimeException("年龄超出了范围"); } } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41测试类
public class ExceptionDemo12 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 键盘录入学生的姓名和年龄,其中年龄为 18 - 25岁, // 超出这个范围是异常数据不能赋值.需要重新录入,一直录到正确为止。 Student s = new Student(); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入姓名"); String name = sc.nextLine(); s.setName(name); while(true){ System.out.println("请输入年龄"); String ageStr = sc.nextLine(); try { int age = Integer.parseInt(ageStr); s.setAge(age); break; } catch (NumberFormatException e) { System.out.println("请输入一个整数"); continue; } catch (AgeOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println(e.toString()); System.out.println("请输入一个符合范围的年龄"); continue; } /*if(age >= 18 && age <=25){ s.setAge(age); break; }else{ System.out.println("请输入符合要求的年龄"); continue; }*/ } System.out.println(s); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# 3.10 自定义异常
自定义异常概述
当Java中提供的异常不能满足我们的需求时,我们可以自定义异常
实现步骤
- 定义异常类
- 写继承关系
- 提供空参构造
- 提供带参构造
代码实现
异常类
public class AgeOutOfBoundsException extends RuntimeException { public AgeOutOfBoundsException() { } public AgeOutOfBoundsException(String message) { super(message); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8学生类
public class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student() { } public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { if(age >= 18 && age <= 25){ this.age = age; }else{ //如果Java中提供的异常不能满足我们的需求,我们可以使用自定义的异常 throw new AgeOutOfBoundsException("年龄超出了范围"); } } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41测试类
public class ExceptionDemo12 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 键盘录入学生的姓名和年龄,其中年龄为 18 - 25岁, // 超出这个范围是异常数据不能赋值.需要重新录入,一直录到正确为止。 Student s = new Student(); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入姓名"); String name = sc.nextLine(); s.setName(name); while(true){ System.out.println("请输入年龄"); String ageStr = sc.nextLine(); try { int age = Integer.parseInt(ageStr); s.setAge(age); break; } catch (NumberFormatException e) { System.out.println("请输入一个整数"); continue; } catch (AgeOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println(e.toString()); System.out.println("请输入一个符合范围的年龄"); continue; } /*if(age >= 18 && age <=25){ s.setAge(age); break; }else{ System.out.println("请输入符合要求的年龄"); continue; }*/ } System.out.println(s); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# 4.Optional
# 4.1获取对象
Optional概述
可能包含或不包含非null值的容器对象
方法介绍
方法名 说明 static Optional of(T value) 获取一个Optional对象,封装的是非null值的对象 static Optional ofNullable(T value) 获取一个Optional对象,Optional封装的值对象可以是null也可以不是null 示例代码
public class OptionalDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { //method1(); //public static <T> Optional<T> ofNullable(T value) //获取一个Optional对象,Optional封装的值对象可以是null也可以不是null //Student s = new Student("zhangsan",23); Student s = null; //ofNullable方法,封装的对象可以是null,也可以不是null。 Optional<Student> optional = Optional.ofNullable(s); System.out.println(optional); } private static void method1() { //static <T> Optional<T> of(T value) 获取一个Optional对象,封装的是非null值的对象 //Student s = new Student("zhangsan",23); Student s = null; //Optional可以看做是一个容器,里面装了一个引用数据类型的对象。 //返回值就是Optional的对象 //如果使用of方法,封装的对象如果为空,那么还是会抛出空指针异常 Optional<Student> optional1 = Optional.of(s); System.out.println(optional1); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# 4.2常用方法
方法介绍
方法名 说明 T get() 如果存在值,返回值,否则抛出NoSuchElementException boolean isPresent() 如果存在值,则返回true,否则为false 示例代码
public class OptionalDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //get() 如果存在值,返回值,否则抛出NoSuchElementException //public boolean isPresent() 判断Optional所封装的对象是否不为空,如果不为空返回true , 否则返回false //Student s = new Student("zhangsan",23); Student s = null; Optional<Student> optional = Optional.ofNullable(s); //如果封装的是一个null,那么通过get方法再次获取会抛出NoSuchElementException。 if(optional.isPresent()){ Student student = optional.get(); System.out.println(student); }else{ System.out.println("Optional封装的对象为空"); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 4.3处理空指针的方法
方法介绍
方法名 说明 T orElse(T other) 如果不为空,则返回具体的值,否则返回参数中的值 T orElseGet(Supplier<? extends T> supplier) 如果不为空,则返回具体的值,否则返回由括号中函数产生的结果 void ifPresent (Consumer<? super T> action) 如果不为空,则使用该值执行给定的操作,否则不执行任何操作 void ifPresentOrElse(Consumer<? super T> action, Runnable emptyAction) 如果不为空,则使用该值执行给定的操作,否则执行给定的基于空的操作 示例代码
public class OptionalDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { //method1(); //method2(); //method3(); //method4(); } private static void method4() { //Student s = new Student("zhangsan",23); Student s = null; Optional<Student> optional = Optional.ofNullable(s); //public void ifPresentOrElse(Consumer<? super T> action, Runnable emptyAction)、 //如果不为空,则使用该值执行给定的操作,否则执行给定的基于空的操作。 optional.ifPresentOrElse(student -> System.out.println(student), ()->System.out.println("为空了")); } private static void method3() { //Student s = new Student("zhangsan",23); Student s = null; Optional<Student> optional = Optional.ofNullable(s); //ifPresent (Consumer<? super T> action) //如果不为空,则使用该值执行给定的操作,否则不执行任何操作 optional.ifPresent(student -> System.out.println(student)); } private static void method2() { Student s = new Student("zhangsan",23); //Student s = null; Optional<Student> optional = Optional.ofNullable(s); //orElseGet(Supplier<? extends T> supplier) //如果不为空,则返回具体的值,否则返回由括号中函数产生的结果 Student student = optional.orElseGet(()-> new Student("lisi" , 24)); System.out.println(student); } private static void method1() { //Student s = new Student("zhangsan",23); Student s = null; Optional<Student> optional = Optional.ofNullable(s); //orElse(T other) 如果不为空,则返回具体的值,否则返回参数中的值 Student student = optional.orElse(new Student("lisi", 24)); System.out.println(student); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
