链表(ts实现)
# 什么是链表
数组(列表)是一种非常简单的存储数据序列的数据结构,而链表是一种动态的数据结构,我们可以从中随意添加和移出项,它会按需进行自动扩容。
数组的数据结构有一个缺点(在大多数语言中):数组一旦被声明,那么它的大小长度就是固定的,不会进行自动扩容。
个别语言,比如JavaScript,Python(列表)的数组有来自语言底层的Array类的方法可以帮我们做扩容这些事情,但背后的情况同样如此。
提示
数组是语言底层就已经存在的内存数据结构,而链表是与数组同级的一种数据结构,与数组是同级的,大部分语言底层是没有实现的(Java的集合框架体系实现了链表),则需要我们手动去实现,不再会和栈和队列一样在内存数据结构的基础上进行拓展和重写,我们要从0开始完成存储数据的一个结构。
# 概念
相对于传统数组,链表的好处在于,添加或移除元素的时候不需要移动其它元素。但是链表需要使用指针。
在数组中我们可以直接访问到任何位置的任何元素,而想要访问链表中的一个元素,则需要从起点(表头)开始迭代链表直到找到所需的元素。
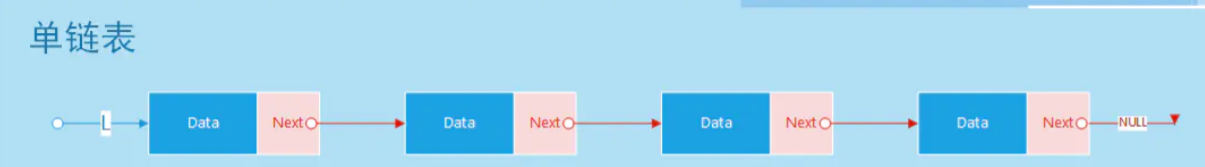
就像火车一样,每节车皮都是链表的元素,车皮间的连接就是指针。
# 链表的创建
# LinkedList类
创建一个LinkedList类作为链表的"骨架"
/**
* description:链表的骨架
* date: 2022/04/11/11:20:00
* author: xinyu
* version: 1.0
**/
class LinkedList<T>{
private count:number; //count用于存储链表中的元素数量
private head:T;//因为链表是动态的,所以需要一个head来保存整个链表的结构,来获取下一个节点的引用
constructor() {
this.count=0;
this.head=undefined;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
因为还需要实现一个indexof方法,即实现链表最核心的一个方法,从起点(表头)开始迭代链表直到找到所需的元素,那么indexof就需要实现字符串或者数字的比较。
因为这个方法之后会经常用到,创建一个utils.ts文件,这个文件用于保存一些经常使用到的方法和类,以及常量。
在utils.ts中export暴露一个function名为defaultEquals
export function defaultEquals<T>(a: T, b: T): boolean {
return a === b;
}
2
3
然后我们在LinkedList类中引入,并把它赋值给构造函数的参数
/**
* description:链表的骨架
* date: 2022/04/11/11:20:00
* author: xinyu
* version: 1.0
**/
import {defaultEquals} from "../utils/util";
class LinkedList<T>{
private count:number; //count用于存储链表中的元素数量
private head:T;//因为链表是动态的,所以需要一个head来保存整个链表的结构,来获取下一个节点的引用
constructor(equalsFn = defaultEquals) {
this.count=0;
this.head=undefined;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# Node类
然后我们还需要一个Node类来作为我们要添加到LinkedList里面的每一项节点。
/**
* description:每一项节点
* date: 2022/04/11/11:48:00
* author: xinyu
* version: 1.0
**/
export class Node<K>{
public element:K;//元素的值 必须为public 否则在LinkedList里无法访问到节点的属性
public next:any;//指向链表中下一个元素的指针
constructor(element) {
this.element=element;
this.next=undefined
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 完整的LinkedList骨架
因为写了Node类,所以把Node类也引入到LinkedList中
/**
* description:链表的骨架
* date: 2022/04/11/11:20:00
* author: xinyu
* version: 1.0
**/
import {defaultEquals} from "../utils/util";
import {Node} from "./Node";
export class LinkedList<T>{
private count:number; //count用于存储链表中的元素数量
private head:Node<T>;//因为链表是动态的,所以需要一个head来保存元素节点的引用
constructor(equalsFn = defaultEquals) {
this.count=0;
this.head=undefined;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
至此整个LinkedList的基本骨架已经写好。
# 添加方法
# push
向尾部添加元素
public push(element:T){
//创建Node对象,项
const node = new Node<T>(element)
let current;//声明一个变量
//判断链表是否为空,为空则把添加的元素赋值为第一个节点
if (this.head==null){
//this.head==null和this.head==null||this.head==undefined等价
this.head=node;
}else {
current=this.head;//前一个节点对象
//一直循环,查找元素的指针是否为null或者undefined
//当循环到一个元素的指针为null或undefined则此元素是最后一个元素
while (current.next!=null){
//courrent.next!=null和courrent.next!=null||courrent.next!=undefined等价
current=current.next; //把里层元素向外抽离
}
//跳出while,此时current就为最后一个元素
//将其next(指向下一个元素的指针)赋为新元素,与新元素建立连接
current.next=node;
}
this.count++;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
提示
Q:this.head是如何赋值上去的?不是赋值在变量current上的吗?
A:
current=this.head,current中复制记录着this.head的值,
while循环前,current和this.head结构一样,
while后,current结构发生改变,且current=current.next;
current整体的内存地址变了,但是里面的对象键值对的地址没有发生改变,
问题关键在于current.next;
.next任然指向的是this.head里面的值,.next是key,记录着this.head中value的内存地址,虽然结构发生改变,但是对象的引用地址没有发生改变,任然是一处改到
# isEmpty,getHead,size,clear
这四个方法比较简单,不多解释。
//返回链表的长度
public size(){
return this.count;
}
//返回链表是否为空
public isEmpty(){
return this.size() === 0;
}
//返回链表的头部节点
public getHead() {
return this.head;
}
// 清空链表
public clear() {
this.head = undefined;
this.count = 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# toString
public toString() {
if (this.head == null) {
return '';
}
let objString = `${this.head.element}`;
let current = this.head.next;
for (let i = 1; i < this.size() && current != null; i++) {
objString = `${objString},${current.element}`;
current = current.next;
}
return objString;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 测试输出
useLinkedList.ts
/**
* description:测试LinkedList
* date: 2022/04/11/13:20:00
* author: xinyu
* version: 1.0
**/
import {LinkedList} from "./LinkedList";
let linkedList = new LinkedList<number>();
console.log(linkedList.isEmpty());//true
linkedList.push(1)
linkedList.push(2)
linkedList.push(3)
linkedList.push(4)
console.log(linkedList.isEmpty());//false
console.log(linkedList.toString());//1,2,3,4
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# this.head的结构
D:\nvm\nodejs\node.exe F:\JavaScriptDataStructure\MyDataStructures\03.LinkedList\useLinkedList.js
Node { element: 1, next: undefined } //第一次push
Node { element: 1, next: Node { element: 2, next: undefined } } //第二次push
Node {
element: 1,
next: Node { element: 2, next: Node { element: 3, next: undefined } } //第三次push
}
Node {
element: 1,
next: Node { element: 2, next: Node { element: 3, next: [Node] } } //第四次push
}
Process finished with exit code 0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
提示
从这个结构可以看出,链表实际上是以对象的键值对的形式从最外层的第一个节点一层一层向里连接的把每个节点连接起来。
往里面的节点也就是所谓排在链表结构后面的节点。
# 添加更多的方法
# getElementAt
返回链表中特定位置的元素,如果链表中不存在这样的元素,则返回undefined
public getElementAt(index: number) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
let node = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index && node != null; i++) {
node = node.next;
}
/**
* 这个for循环等价于:
* for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
* if(node!=null){
* node = node.next;
* }else{
* break;
* }
}
*/
return node;
}
return undefined;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# insert
特定位置插入元素。
public insert(element: T, index: number) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new Node<T>(element);
if (index === 0) {
const current = this.head;
node.next = current;
//更新this.head
this.head = node;
} else {
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
node.next = previous.next;
previous.next = node;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# removeAt
移出指定位置元素
public removeAt(index: number) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
this.head = current.next;
} else {
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
current = previous.next;
previous.next = current.next;
}
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return undefined;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# remove
删除一个元素,并非指定位置。
public remove(element: T) {
const index = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
2
3
4
# indexOf
返回元素在链表中的索引
public indexOf(element: T) {
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < this.size() && current != null; i++) {
if (this.equalsFn(element, current.element)) {
return i;
}
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 双向链表
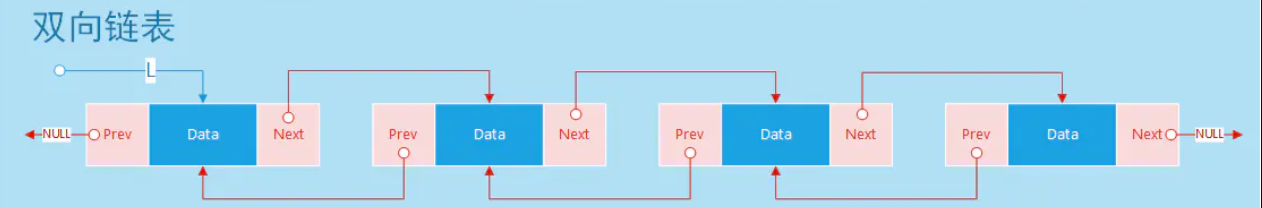
双向链表和普通链表的区别在于,单向链表的一个节点只有链向下一个节点的链接;而在双向链表中,链表是双向的:一个链向下一个元素,另一个链向前一个元素,双向链表需要同时控制next(后一个)和prev(前一个)两个指针
# 双向链表的创建
# DoublyNode
双向链表的主要改变是节点的改变,所以先更改Node。
创建一个名为DoublyNode的类,因为是在Node的基础上做的修改,使用继承。
增加一个prev属性用来保存前一个节点的引用,作为连接。
/**
* description:双向链表的节点
* date: 2022/04/13/11:08:00
* author: xinyu
* version: 1.0
**/
import {Node} from "./Node";
export class DoublyNode<K> extends Node<K>{
public prev:K;
constructor(element,prev) {
super(element);
this.prev=prev;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# DoublyLinkedList
创建一个名为DoublyLinkedList的类,因为很多方法都是和LinkedList一样,也使用继承。
添加一个tail用来保存链表最后一个元素的引用。
/**
* description:双向链表
* date: 2022/04/13/11:06:00
* author: xinyu
* version: 1.0
**/
import {LinkedList} from "./LinkedList";
import {defaultEquals} from "../utils/util";
export class DoublyLinkedList<T> extends LinkedList <T>{
public tail:T
constructor(equalsFn=defaultEquals) {
super(equalsFn);
this.tail=undefined;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
